查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过






Stroke & Vascular Neurology(SVN)最新上线文章“Impaired glymphatic system as evidenced by low diffusivity along perivascular spaces is associated with cerebral small vessel disease: a population-based study”,来自首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院、国家神经系统疾病临床医学研究中心王伊龙教授、潘岳松教授团队等。

本研究旨在调查社区人群中类淋巴系统与脑小血管病(cerebral small vessel disease, CSVD)的发生、严重程度和神经影像学表型的关系。
研究共纳入2219例年龄在50~75岁之间、参与了多血管床评估与认知损伤和血管事件社区人群队列研究(PolyvasculaR Evaluation for Cognitive Impairment and vaScular Events, PRECISE)的社区居民。基于弥散张量成像测量沿血管周围间隙的弥散率(diffusivity along perivascular spaces based on diffusion tensor imaging, DTI-ALPS指数),以评估类淋巴通路。应用两种不同的CSVD评分(Wardlaw评分:0~4分;Rothwell评分:0~6分)来评估CSVD的发生及严重程度,这些评分综合了4个常见的CSVD神经影像学特征,包括白质高信号(white matter hyperintensity, WMH)、血管周围间隙扩大(enlarged perivascular spaces, EPVS)、腔隙、脑微出血;此外,评估了脑萎缩(Brain atrophy, BA)。采用二元或有序logistic回归分析探究DTI-ALPS指数与CSVD的关系。
研究结果显示,受试者平均年龄为61.3岁(SD 6.6),其中1019例(45.9%)为男性。平均DTI-ALPS指数为1.67(SD 0.14)。与第四四分位数(Q4)相比,DTI-ALPS指数位于第一四分位数(Q1)的个体发生CSVD(Wardlaw评分:OR 1.77, 95% CI 1.33-2.35, p<0.001;Rothwell评分:OR 1.80, 95% CI 1.38-2.34, p<0.001)、CSVD总负担(Wardlaw评分:common OR (cOR) 1.89, 95% CI 1.43-2.49, p<0.001;Rothwell评分:cOR 1.95, 95% CI 1.51-2.50, p<0.001)的风险更高。此外,DTI-ALPS指数位于Q1的个体发生WMH、腔隙、基底神经节EPVS和BA的风险均增加(所有p<0.05)。
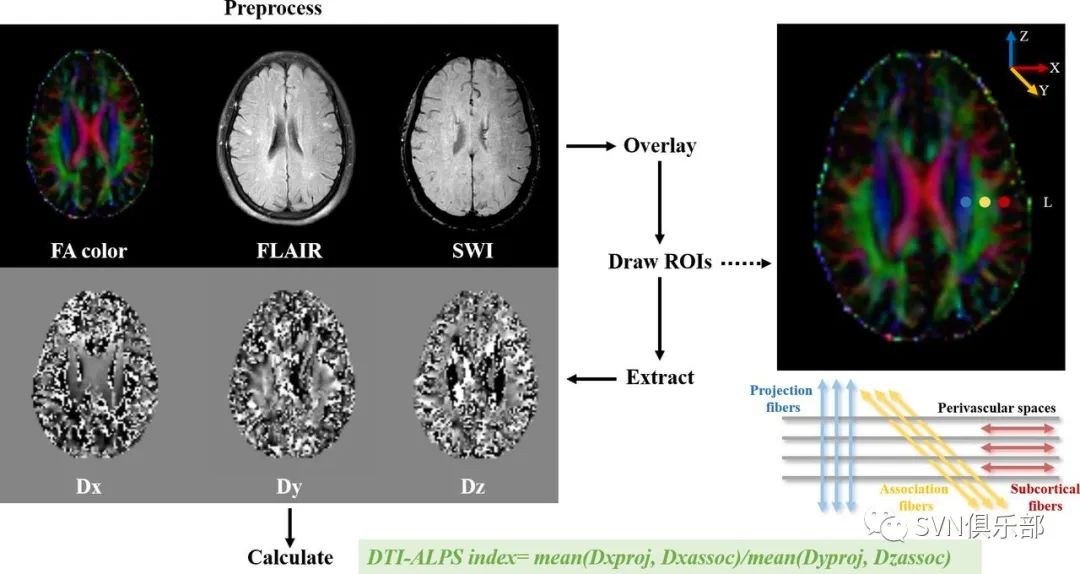
Figure 1.The assessment of glymphatic system by calculating the DTI-ALPS index. DTI-ALPS, diffusivity along the perivascular spaces based on diffusion tensor imaging; FA, fractional anisotropy; FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; ROI, regions of interest; SWI, susceptibility-weighted imaging.
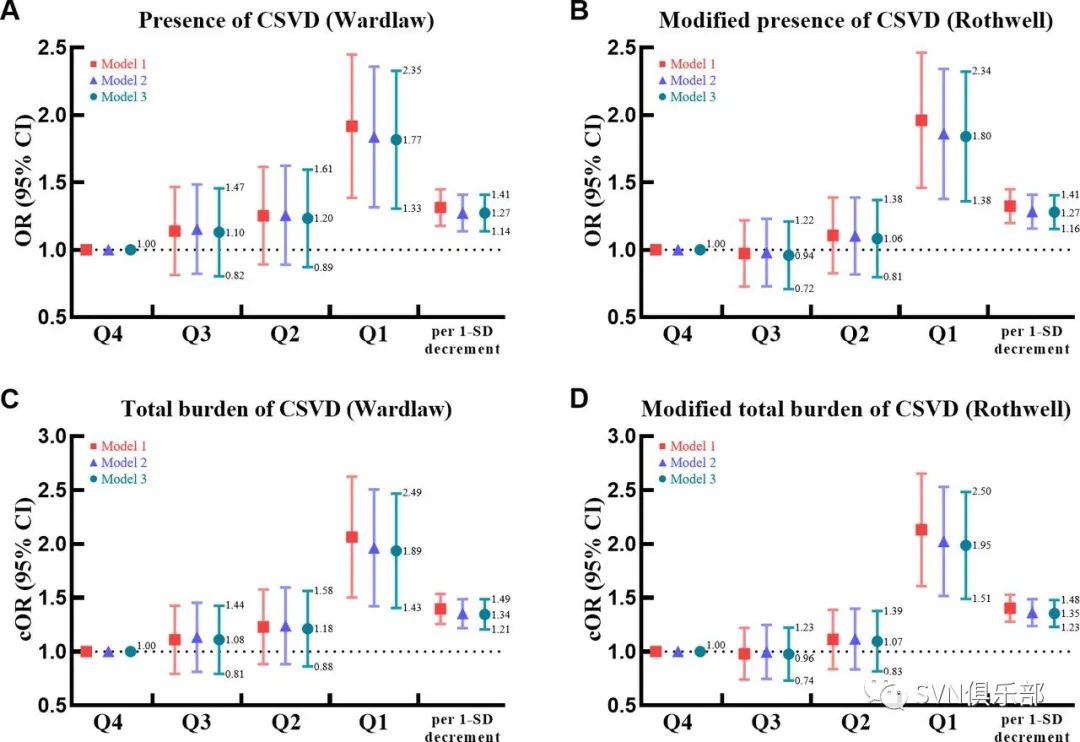
Figure 3. The DTI-ALPS index in association with the presence and severity of CSVD. Forest plots present ORs/cORs for the associations of the DTI-ALPS index with the presence of CSVD (A), modified presence of CSVD (B), total CSVD burden (C) and modified total CSVD burden (D). The colourful lines indicate 95% CIs of ORs/cORs. Model 1 adjusted for age and sex; model 2, vascular risk factors; model 3, current medications. cOR, common OR; CSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; DTI-ALPS, diffusivity along the perivascular spaces based on diffusion tensor imaging.
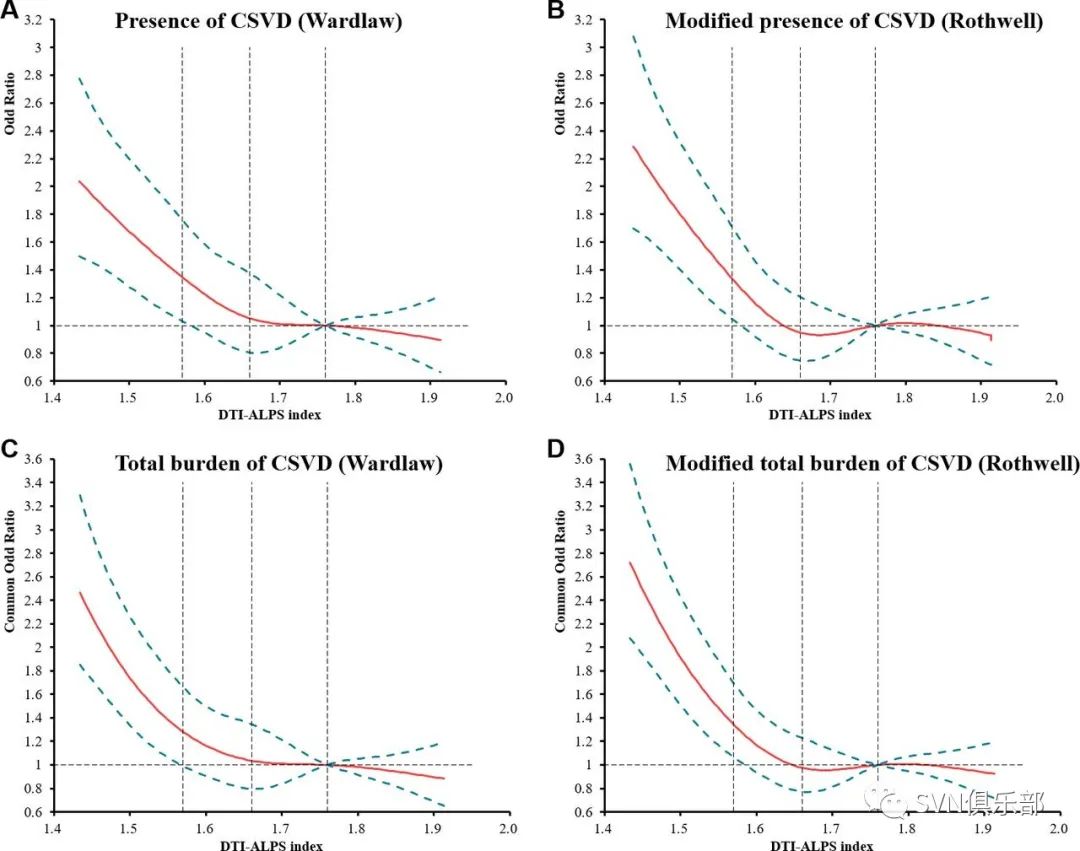
Figure 4. Restricted cubic spline plots for the associations of the DTI-ALPS index with the presence and severity of CSVD. Adjusted ORs/cOR for presence of CSVD (A), modified presence of CSVD (B), total CSVD burden (C) and modified total CSVD burden (D) based on restricted cubic spines with 5 knots at 5th, 25th, 50th, 75th and 95th percentiles of the DTI-ALPS index. The solid line indicates adjusted ORs/cORs, and the dashed lines the 95% CI bands. Reference is the first quartile of ALPS index. The vertical dashed lines indicate the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles of DTI-ALPS index. Data were fitted using a binary/ordinal logistic regression model of restricted cubic spline with five knots (the 5th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 95th percentiles) for the DTI-ALPS index after adjusting for all potential confounders. The lowest 5% and highest 5% of participants are not shown. cOR, common OR; CSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; DTI-ALPS, diffusivity along the perivascular spaces based on diffusion tensor imaging.
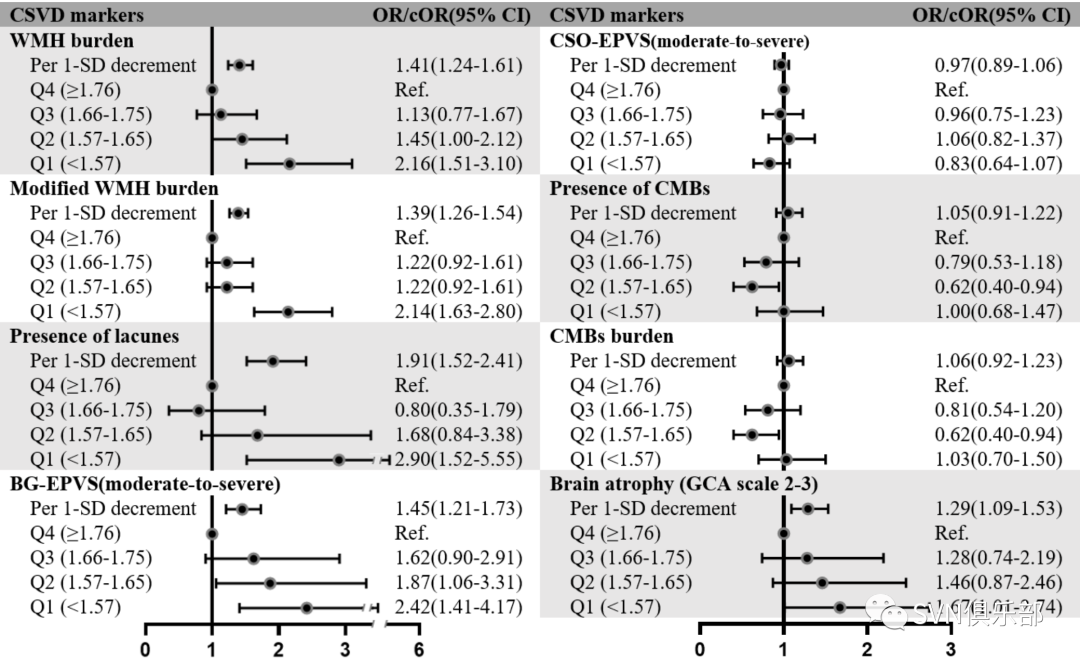
Figure 5. The DTI-ALPS index in association with neuroimaging phenotypes of CSVD. Forest plots present ORs/cORs for the associations of the DTI-ALPS index with different neuroimaging marker of CSVD. The black lines indicate 95% CIs of ORs/cORs. Multivariable logistic regression model adjusted for all potential confounders. BG-EPVS, basal ganglia-EPVS; CSO-EPVS, centrum semiovale-EPVS; CMBs, cerebral microbleeds; cOR, common OR; CSVD, cerebral small vessel disease; DTI-ALPS, diffusivity along the perivascular spaces based on diffusion tensor imaging; EPVS, enlarged perivascular space; GCA, global cortical atrophy scale; WMH, whiter matter hyperintensity.
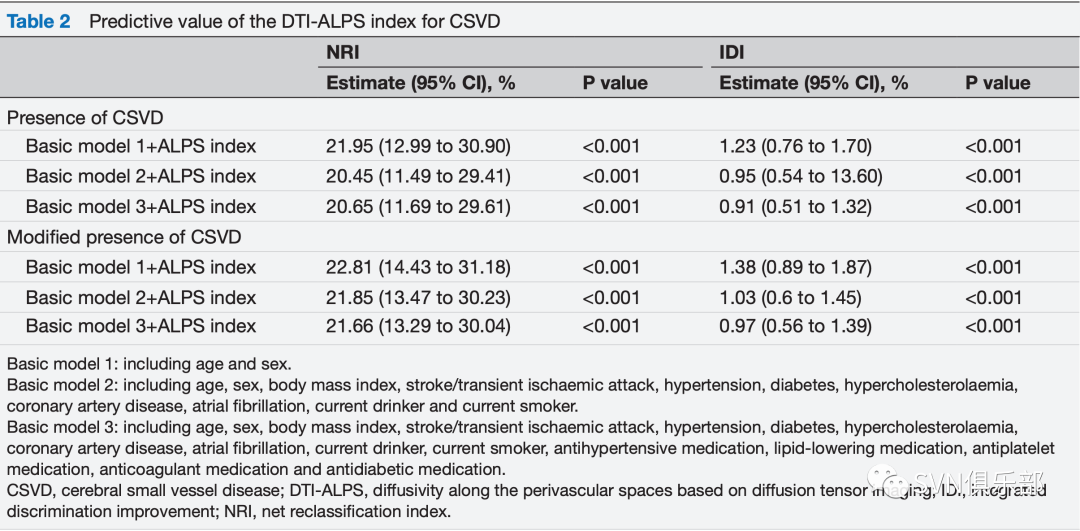
研究结论,较低的DTI-ALPS指数与CSVD的发生、严重程度和典型的神经影像学标志物相关,这意味着在一般老龄化人群中,类淋巴系统的损伤可能与CSVD相关病理生理机制存在相互作用。

来源:SVN俱乐部
转载已获授权,其他账号转载请联系原账号
查看更多